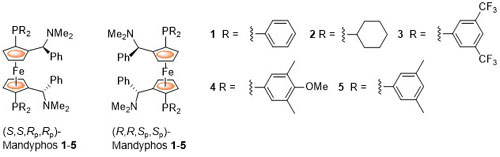
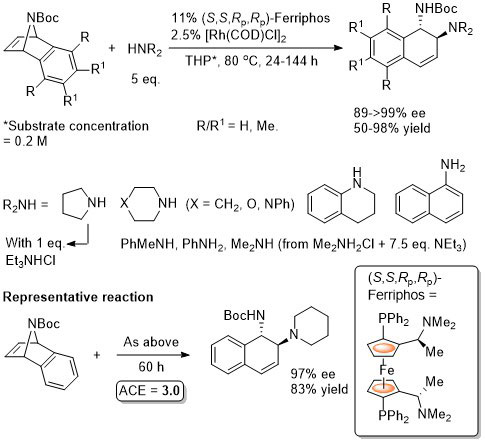
The parent ligand 1 was first reported by Schwink and Knochel and was later described as one of a class of FERRIPHOS ligands. Later publications rebranded the following structures differing only in the nature of the phosphorus substituents as MandyPhos ligands. The following lists reactions, organised by metal (Pd, Rh, Ru, Ir, Cu, Ni) for which the application of these ligands has resulted in >80% ee. ACE = Asymmetric Catalytic Efficiency. Literature covered until 2020 (21 entries).
Palladium
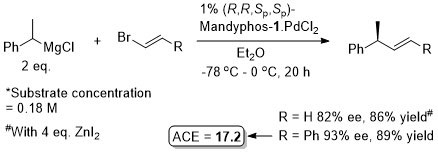
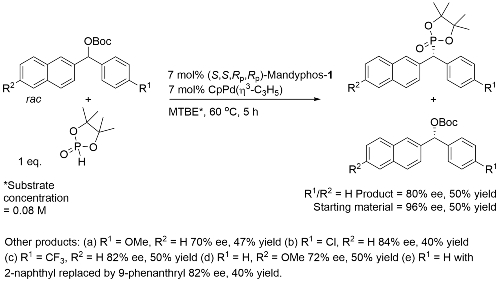
Pd-Cross-coupling CEJ98-4-950
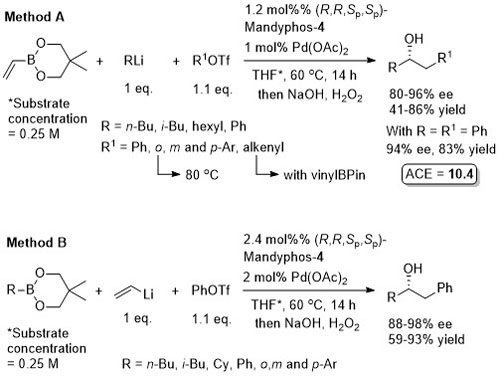
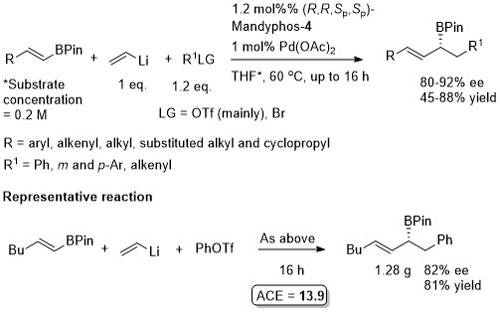
Pd – Conjugative cross-coupling Science16-351-70
The presence of lithium halide salts (even at 1-2 mol%) markedly erodes conjugative coupling efficiency. Later found that this inhibition may be overcome by the addition of NaOTf or KOTf such that vinyllithium may be generated from the addition of t-BuLi (2 eq.) to vinyl bromide and conjugative cross-coupling carried out with 2.2 eq. of KOTf. See JACS17-39-3153.
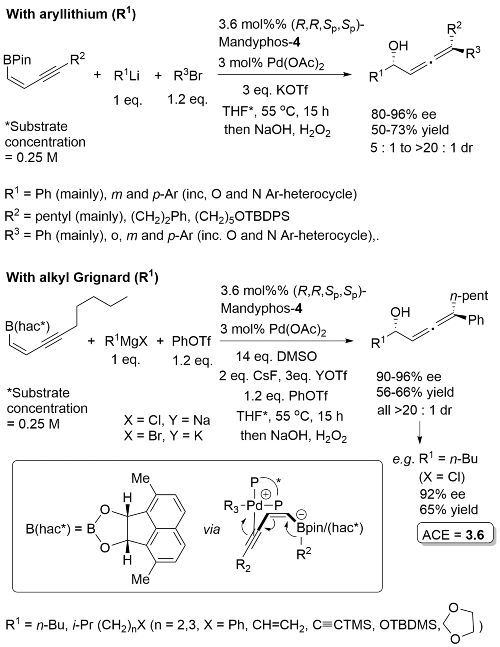
Allyl boron reagents containing 1- or 2-(Z)-substituents resulted in ee values <80%. Halide free vinyllithium employed generated from tetravinylstannane by Li-Sn exchange. Vinyl magnesium chloride and vinyllithium generated from vinyl bromide (+ 2 eq. t-BuLi) also used successfully provided 2 eq. of NaOTf or KOTf added, respectively (and at 2 mol% catalyst loading).
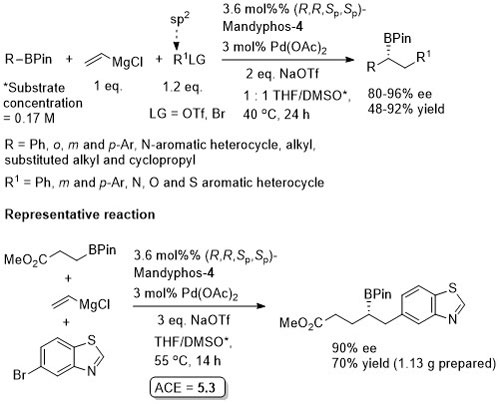
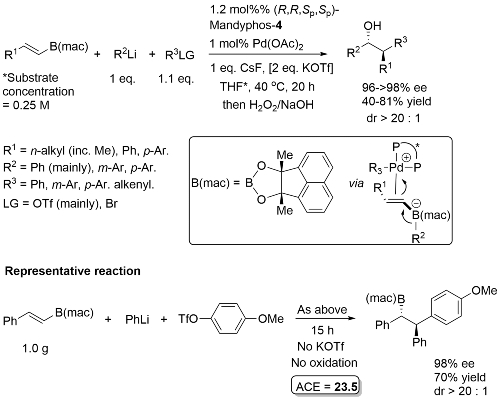
The diol mac (methylated acenaphthoquinone) developed to suppress competitive Suzuki-Miyaura (SM) cross-coupling. Remaining mass balance from SM reaction which was more significant with electron-deficicent electrophiles (and only SM with “ate” complexes containing alkyl migrating groups). KOTf added if LG = Br, or R2Li generated from RBr by halogen-lithium exchange with t-BuLi. In addition to an alcohol, B(mac) product from the representative reaction also converted stereospecifically into -NH(Boc) and CH2B(mac). This process has the potential of sponsorship from McDonalds…
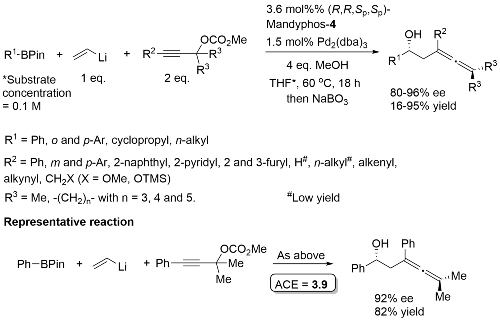
MeOH replaced by trifluoroethanol where R1 = alkyl.
High ee but lower dr with trans-enyne derived boronates. Conditions for aryl migration ineffective for alkyl migration – hence the development of hac*.
Pd – Benzylic Phosphorylation OL18-20-3553
Process rationalised as a starting material kinetic resolution with an element of dynamic kinetic resolution in product formation via interconverting η3-allyl (naphthyl) intermediates.
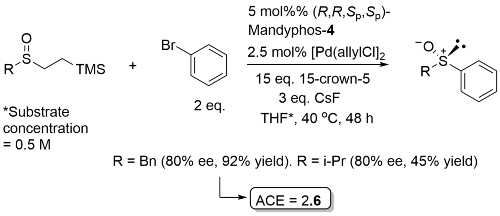
Pd - Arylation of Sulfenate Anions OL19-21-960
Just two examples with ee ≥ 80. Process mostly demonstrated with R = Ar with both alkenyl and aryl electrophiles for which the ligand used was Josiphos-3.
Rhodium
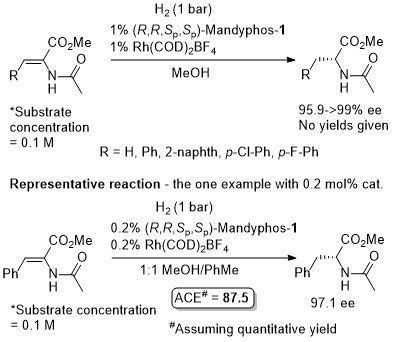
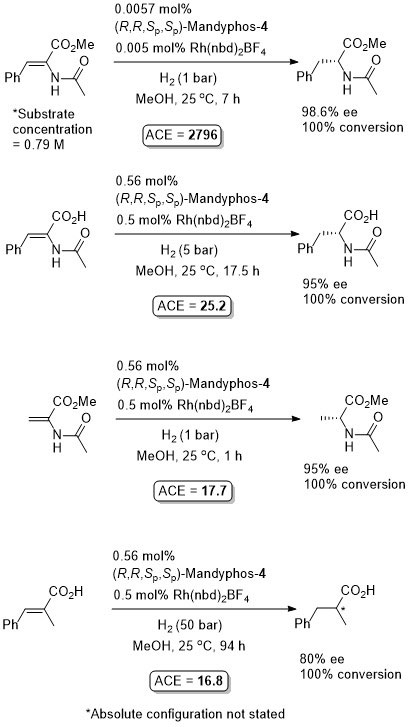
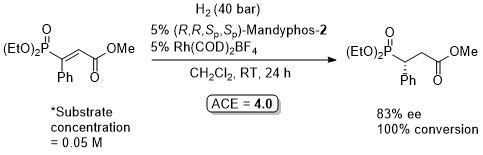
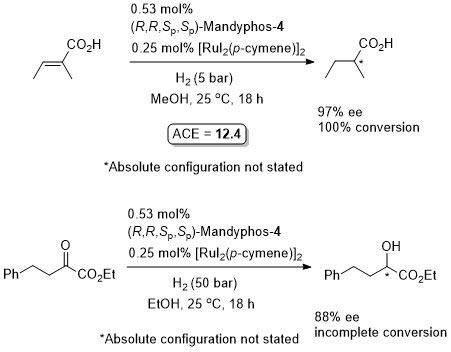
Rh-Hydrogenation TA98-10-375
Enamide MAC (methyl α-acetamidocinnamate) also hydrogenated (H2 – 1 bar) to give product in 99% ee with Mandyphos-1 and [Rh(NBD)2]BF4 in biphasic 1 : 1 [omin]BF4/H2O – see ASC04-346-1481.
Absolute configuration assigned by comparison to data in CEJ09-15-10983. Josiphos-3 has also been applied to this reaction.
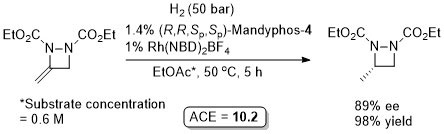
Rh – Asymmetric ring opening JACS06-128-6837
The ligand used is described as Ferriphos and is closely related to Mandyphos-1. It is reasonable to suggest that the latter woud give similar results (e.g. – see next entry). Ferriphos not commercially avaialble. For synthesis see TA99-10-375 and earlier work by Hayashi in CC89-495.
Ruthenium
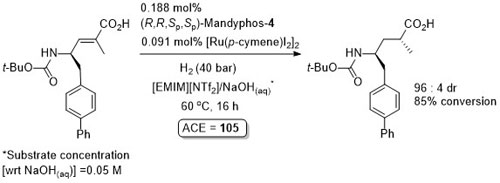
Ru – Hydrogenation TA04-15-2299
Diastereoselective hydrogenation in a biphasic system with the product isolated after separation of the aqueous phase from ionic liquid [EMIN][NTf2] followed by addition of HCl(aq). Catalyst phase reused for an additional 6 cycles with little loss of selectivity and conversion (so ACE = approximately 700).
Iridium
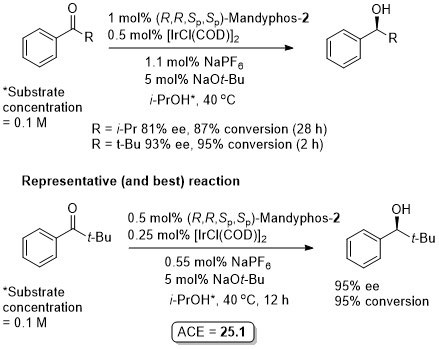
Ir – Transfer hydrogenation CEJ08-14-10388
Absolute configuration assigned by comparison to the result obtained for the reduction under the 1% Ir/ligand conditions of acetophenone [72% ee (S)].
Copper
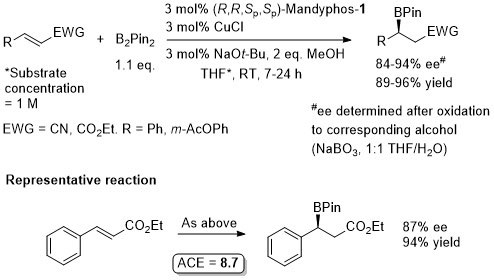
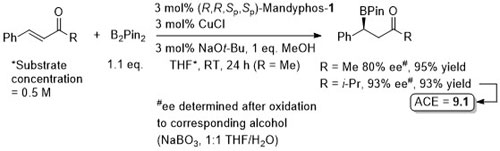
Cu – Beta borylation Angew08-47-145
Similar ee values obtained with Josiphos-1.
Josiphos-1 also applied successfully to this reaction (more examples).
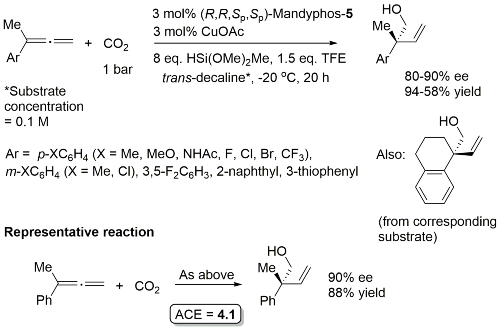
Cu – Hydroxymethylation with CO2 CEJ19-25-13874
Product configuration = R (not clearly represented in the manuscript). Ligand used identified as (R,R)-xylyl-Mandyphos. Structure in paper suggests this is the (R,R,Sp,Sp)-enantiomer, but not as clear as it might be.
Nickel
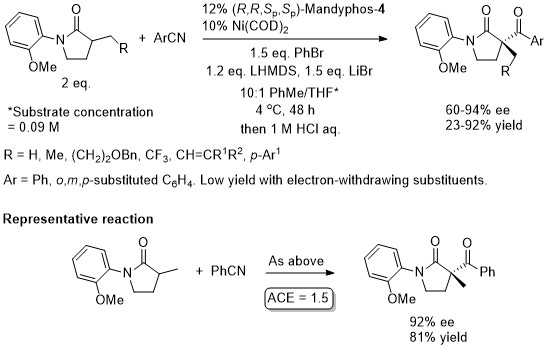
Ni – Lactam C-acylation JACS16-138-8997